If you own a business in the Philippines, you must be familiar with Withholding Tax on Compensation (WTC). This tax is levied on certain payments made by employers to their employees based on the compensation tax table. The WTC is used to compute the income tax that an employee owes for the year. Here are the basic guidelines on how to compute withholding tax on compensation. Keep reading!
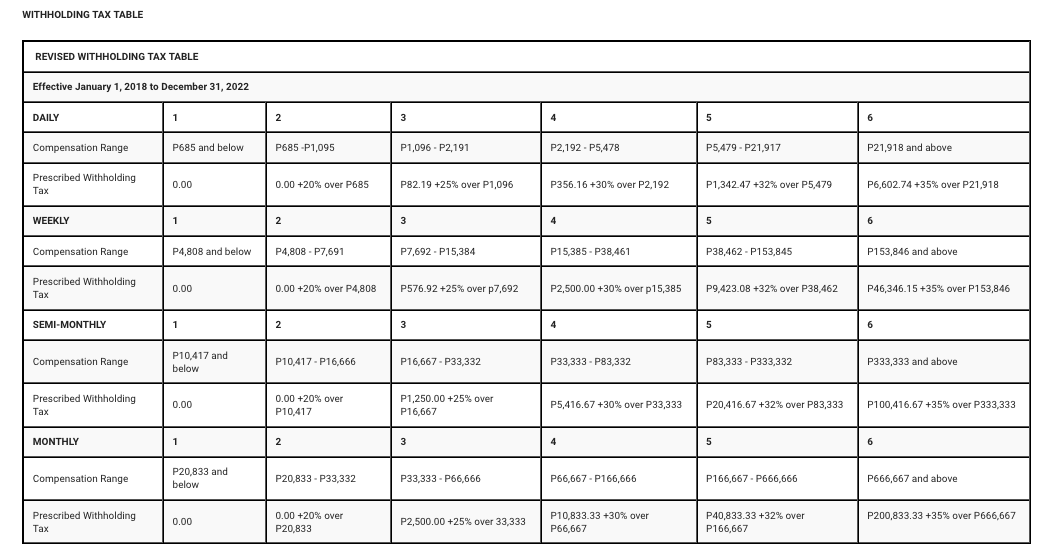
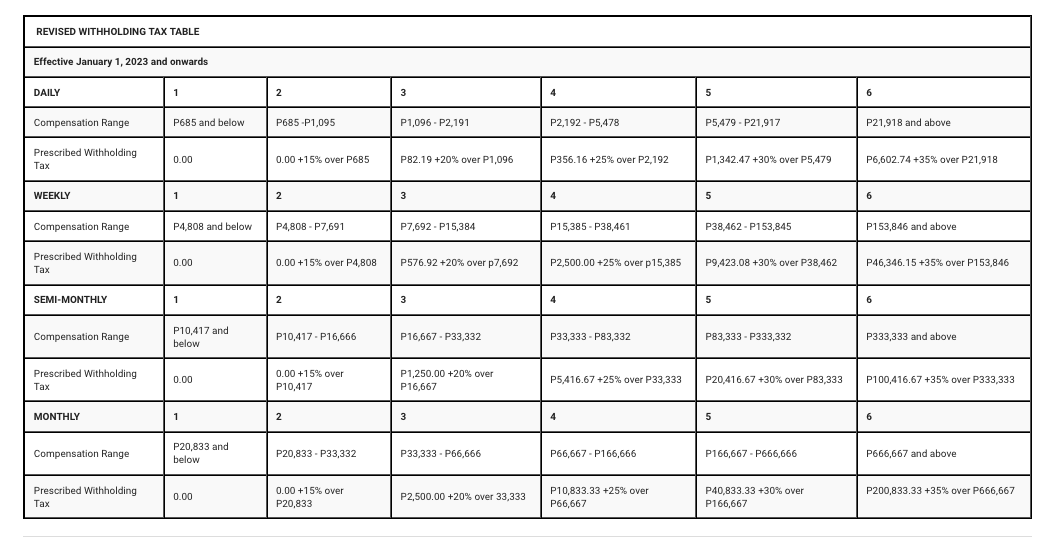
Compensation Tax Table
Compensation includes salaries, wages, bonuses, allowances, and other benefits received by an employee from their employer. The WTC is computed using a Compensation Tax Table and a Withholding Tax Compensation Table.
The Compensation Tax Table lists the amount of tax an employee owes for the year based on their compensation income. The Withholding Tax Compensation Table shows the amount of tax an employer must withhold from an employee’s salary.
What Is Withholding Tax On Compensation Income
Withholding tax is a tax that businesses withhold from employee compensation payments. Withholding tax is to ensure that employees pay their taxes on time. Withholding tax also allows companies to recover some of the costs associated with collecting and remitting taxes to the government.
Related: 8% Income Tax Rate Option: How It Affects You
Paying your taxes is a responsibility that doesn’t just apply to individuals anymore. It’s also valid for employers and their employees alike! The government requires all companies, big or small, to take taxes from what they earn. This is so the government can make sure people don’t avoid taxes. The money that is taken out is called withholding taxes.
The BIR Form 2316 is a different document from the Annual ITR. The former indicates total income and taxes withheld filed by an individual’s employer. In contrast, It will use this last one to file its tax return once they’re done with it, for they do not owe any interest or penalties on what was unpaid due when filing time comes around again next year!
How To Compute Withholding Tax on Compensation Using Compensation Tax Table
Final Withholding Tax is a tax on compensation that is final, due, and payable. The employer is liable for the withholding and remittance of the tax to the government. The Final Withholding Tax shall be based on the total compensation paid by the employer to an employee, whether in cash or property, with certain exceptions as provided for in the National Internal Revenue Code (NIRC). The Final Withholding Tax Due shall be computed using the following formula:
Final Withholding Tax Due = (Gross Compensation x Applicable Tax Rate) – Non-taxable allowance and benefits.
The steps below will guide you on withholding tax on compensation paid to your employees in the Philippines.
1) Compute the gross compensation weekly, bi-weekly, semi-monthly, or monthly.
2) Determine an employee’s taxable compensation income base by subtracting any allowable de minimis benefits and qualified additional exemptions from their gross compensation income. The allowable amount is up to 90,000 deminimis benefits.
3) Multiply the result in step 2 by the applicable withholding tax rate to determine an employee’s final withholding tax liability using the compensation tax table below.
4) Subtract any advance taxes withheld during the year from the final withholding tax liability. The difference is the amount of tax the employer must withhold from the employee’s compensation and remit to the BIR.
REMEMBER: Withholding Tax on Compensation is a responsibility that doesn’t go away, so if you don’t make the payment on time, it’ll slap you with penalties and interest.
You are an employee who earns a monthly taxable salary of PHP 30,000. Your employer withholds PHP 1,833.40 as withholding tax from your salary every month. At the end of the year, you will have paid PHP 22 000 in withholding tax (PHP 1,833.40 x 12 months).
When you file your income tax return, you will receive no tax refund since the tax withhold is the same amount of tax to be paid at the end of the year. This is because the amount of tax you owe for the year is PHP 22,000 (PHP 30,000 x 12 months-250,000 * 20% income tax rate). The amount of tax you have already paid through withholding is PHP 22,000.
Filing Requirements for Withholding Tax on Compensation
The total taxes withheld using compensation tax table must be reported monthly using BIR Form 1601C. This form is due by the 10th day of each month after withholding, except for December, when it has to come back before January 15 following that same fiscal year’s end date (June 30).
Employers will also need to report their compensation tax amount totaled throughout all employees’ wages during one calendar year, with this reporting requirement coming down just prior: to January 31 using the BIR Form 1604C.
Related: The Most Common Errors In Using BIR eFPS- How To Fix Them
Types of Withholding Tax On Compensation
There are three main types of withholding tax on compensation:
Expanded Withholding Tax
It is commonly known in the Philippines as withholding tax on certain income payments. The Withholding of Creditable Tax at Source, or called Expanded Withholding Tax, is a tax paid by a payor-corporation/person to the government on income paid to natural or juridical persons residing in the Philippines. This tax will be credited against the taxpayer’s income tax liability for the taxable year.
This tax is then remitted to the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR). In other words, an expanded withholding tax is another way for the government to ensure taxpayers are paying their fair share. But don’t worry; an expanded withholding tax is not something you have to pay out of your pocket. The payor-corporation/person will withhold the amount of expanded withholding tax due from your income payment and remit it to the BIR on your behalf.
Withholding Tax on Compensation
Withholding Tax on Compensation in the Philippines is a tax imposed on certain types of compensation paid to employees. The tax is withheld by the employer and remitted to the government.
The Withholding Tax on Compensation is one of the significant sources of revenue for the government. The Withholding Tax on Compensation is imposed on all forms of compensation, including salaries, allowances, bonuses, commissions, and other benefits. The Withholding Tax on Compensation is progressive, with higher rates applying to higher compensation levels.
Final Withholding Tax
Final Withholding Tax is a withholding tax prescribed on certain income payments. It is not creditable against the income tax due of the payee on other income subject to regular tax rates for the taxable year. Income Tax withheld constitutes the entire and final payment of the Income Tax due from the payee on the particular income subjected to final withholding tax.
Final Withholding Taxes are typically levied on gaming winnings, prizes, and commissions earned by real estate brokers. It is also commonly imposed on foreign nationals working in the Philippines.
What records need to be kept concerning withholding tax on compensation payments?
Employers must keep records of all Withholding Tax on Compensation payments made to employees. It must keep these records for five years from the date of payment.
It must include the following information in Withholding Tax on Compensation records:
- Name, address, and tax identification number of the employee
- Amount of compensation paid
- Amount of Withholding Tax on Compensation withheld
- Date of payment
- Period to which the payment relates
Tips For Complying With Withholding Tax On Compensation Requirements
Here are some tips to help you comply with Withholding Tax on Compensation requirements:
Keep accurate records of all Withholding Tax on Compensation payments
As an employer, you are responsible for keeping correct documents of all Withholding Tax on Compensation payments made to employees. It must keep these records for five years from the date of payment. Use always the updated compensation tax table.
Related: Common Double Entry Accounting Mistakes-And How to Avoid Them!
Ensure that Withholding Tax on Compensation is withheld from all eligible employees
Withholding Tax on Compensation is a tax imposed on certain types of compensation paid to employees. Ensuring that Withholding Tax on Compensation is withheld from all eligible employees is essential.
Make sure that Withholding Tax on Compensation payments are remitted to the government promptly
Withholding Tax on Compensation payments must be remitted to the government on time. Failure to do so may result in penalties and interest charges.
Keep up to date with changes in Withholding Tax on Compensation rates
Withholding Tax on Compensation rates is subject to change from time to time. As such, it is essential to keep up to date with changes in Withholding Tax on Compensation rates.
Penalties for failure to comply with withholding tax on compensation requirements
If you fail to comply with Withholding Tax on Compensation requirements, you may be liable for penalties and interest charges.
Related: 25 Ways to Reduce Your Tax Burden as a Small Business in the Philippines
The following are some of the most common penalties that it may impose for failure to comply with Withholding Tax on Compensation requirements:
Failure to withhold Withholding Tax on Compensation: If you fail to withhold Withholding Tax on Compensation from eligible employees, you may be liable for a penalty of PHP 1,000.
Failure to remit Withholding Tax on Compensation: If you fail to remit Withholding Tax on Compensation payments to the government on time, you may be liable for a penalty of 10% of the tax due, plus interest charges.
Failure to keep accurate records: If you fail to keep correct documents of all Withholding Tax on Compensation payments made to employees, you may be liable for a penalty of PHP 1,000.
Failure to file an annual return: If you fail to file a yearly return on Withholding Tax on Compensation, you may be liable for a penalty of PHP 5,000.
Conclusion
This blog post discussed the basics of withholding tax on compensation in the Philippines. We explained how to compute WTC and the applicable rates for each type of compensation based on the compensation tax table. If you need help filing your taxes, our team at Taxguro is here to assist you. Contact us today and let us help you take care of all your tax needs!
Recommended: How to Register Your Business as Barangay Micro Business Enterprise (BMBEs)